If you’re looking to add some heat to your culinary creations, ghost peppers may be just the thing for you! In this guide, we’ll walk you through the basics of how to grow ghost peppers, from planting seeds to caring for the plants and dealing with common problems.
Basic Information
Before we dive into the details of how to grow ghost peppers, let’s start with some basic information about these fiery peppers. Also known as Bhut Jolokia, ghost peppers are one of the hottest chili peppers in the world, and growing them can be a rewarding and exciting experience.
Here’s a quick reference table to give you an overview of what you need to know:
| Topic | Information |
|---|---|
| Common names | Ghost peppers, Bhut Jolokia |
| Scientific name | Capsicum chinense |
| Days to harvest | 90-120 days |
| Light | Full sun (at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day) |
| Soil | Well-draining, fertile soil with a pH of 6.0-6.5 |
| Water | Moderate watering, avoiding overwatering |
| Fertilizer | Fertilizer with a higher phosphorus and potassium ratio when fruiting |
| Pests | Aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies |
| Diseases | Powdery mildew, bacterial spot, and viral diseases |
Now, let’s dive into the details of how to grow ghost peppers from seeds and care for the plants throughout their growth cycle.
How to Grow Ghost Peppers from Seed
Starting ghost pepper seeds indoors is a great way to get a head start on the growing season and ensure that your plants have enough time to mature. This is especially important if you have a short growing season. Peppers seeds should be started indoors about 10-12 weeks before the last frost in your area.
Follow these simple steps to successfully start ghost pepper seeds indoors
- First, gather your supplies:
- Seed starting trays or 4″ nursery pots
- Seed starting mix
- Water spray bottle
- Humidity dome
- Seedling grow light
- Seedling heat mat and temperature controller
- Moisten the soil: It’s always best to moisten the soil before filling the containers. To guage proper soil moisture, squeeze a handful of soil. You should get only a couple drops of water if the soil has the proper moisture level.
- Prepare the seed tray or pots: Fill the trays or pots with moist seed starting mix. Gently press down the soil to remove any air pockets.
- Sow the seeds: Make a hole in the soil about a 1/4″ deep in the center of each cell or pot. Place two ghost pepper seeds in each hole and cover lightly with soil. If both seeds germinate, you can cull the weaker seedling later but this method helps ensure you get at least one seedling per cell.
- Cover the tray or pots: Place a humidity dome over the seed trays or pots to create a greenhouse-like environment that will help retain moisture and promote germination.
- Provide light and warmth: Pepper seeds require warm temperature to germinate. Use of a heat mat is recommended. Pepper seeds germinate much better at temperatures between 75-85F.
- Maintain moisture and ventilation: Check the moisture level of the soil regularly and water as needed to keep it evenly moist, but not waterlogged. Remove the humidity dome for a few minutes each day to allow for ventilation and prevent mold or damping-off disease.
- Be patient and wait for germination: Ghost pepper seeds can take anywhere from 7 to 21 days to germinate, depending on the temperature and other growing conditions. Be patient and resist the urge to overwater or disturb the seeds during this period.
- Provide high quality light: As soon as the seedlings pop up, be sure and provide a strong source of light. The light from a windowsill is rarely sufficient, even a south facing window. We recommend using a good quality seedling grow light. It’s worth the investment if you plan on starting garden seeds every year.
Transplanting into the Garden

Hardening Off
Before transplanting your ghost pepper seedlings into the garden, it’s important to harden them off to help them adjust to the outdoor conditions.
Hardening off is the process of gradually acclimating the seedlings to the outdoor environment by exposing them to increasing amounts of sunlight, wind, and temperature fluctuations over a period of 7-10 days.
Start by placing the seedlings in a shady spot outdoors for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the exposure to sunlight and outdoor conditions each day. Make sure to protect the seedlings from harsh winds and extreme temperatures during this process.
By the end of the hardening off period, the seedlings should be ready to be transplanted into the garden.
Planting
Once the seedlings have grown to about 4-6 inches in height and have developed at least two sets of leaves, they can be transplanted into the garden. Choose a sunny spot in your garden with well-draining, fertile soil.
Prepare the planting hole by loosening the soil and adding some compost or well-rotted manure for added nutrients. When planting ghost pepper seedlings in the garden, make sure to space them at least 18-24 inches apart to allow for proper airflow and to prevent overcrowding.
Dig a hole in the prepared soil that is slightly larger than the size of the root ball of your seedling. Place a small amount of bone meal, blood meal, and greensand into the planting hole. These are great slow release of nutrients.
Gently remove the seedling from its container, being careful not to damage the roots, and place it in the hole. Fill the hole with soil and gently press down to secure the seedling in place. Water the transplanted seedling thoroughly to help it establish in its new location.
Light and Temperature to Grow Ghost Peppers
Ghost peppers require plenty of sunlight and warm temperatures to grow and produce fruits. Here are some tips on providing the right light and temperature conditions for your ghost pepper plants:
Sun
Ghost peppers need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day to thrive. Choose a sunny spot in your garden that receives ample sunlight throughout the day.
Temperature
Ghost peppers thrive in warm temperatures, ideally between 70-85°F (21-29°C) during the day and 60-70°F (15-21°C) during the night. They are sensitive to frost and cold temperatures, so it’s important to plant them after the last frost date in your area and provide protection if there is a sudden drop in temperature.
Soil, Water, and Nutrients for Ghost Peppers
Soil
Ghost peppers prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. The soil pH should be slightly acidic to neutral, ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. Before planting, amend the soil with compost or well-rotted manure to improve its fertility and drainage.
Water
Water the ghost peppers consistently, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overwatering, as it can cause root rot and other diseases. Water deeply and less frequently rather than frequent shallow watering.
Ghost peppers generally require moderate water, but the watering frequency may vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and rainfall.
Fertilizer to Grow Ghost Peppers
Ghost peppers are heavy feeders and require regular fertilization for optimal growth and fruit production. While the peppers are growing only foliage, use fish emulsion or a balanced, water soluble fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Once the plants start to grow fruit, start using a fertilizer with less nitrogen and more phosphorus and potassium. Tomato fertilizers usually contain the proper nutrient ratios required by peppers. In addition, the periodic use of CalMag can help prevent blossom end rot.
Fertilize the ghost pepper plants every 2-3 weeks throughout the growing season. However, be careful not to over-fertilize, as it can cause nutrient burn and damage the plants. Follow the manufacturers mixing instructions.
Pest and Disease Control: Grow Ghost Peppers
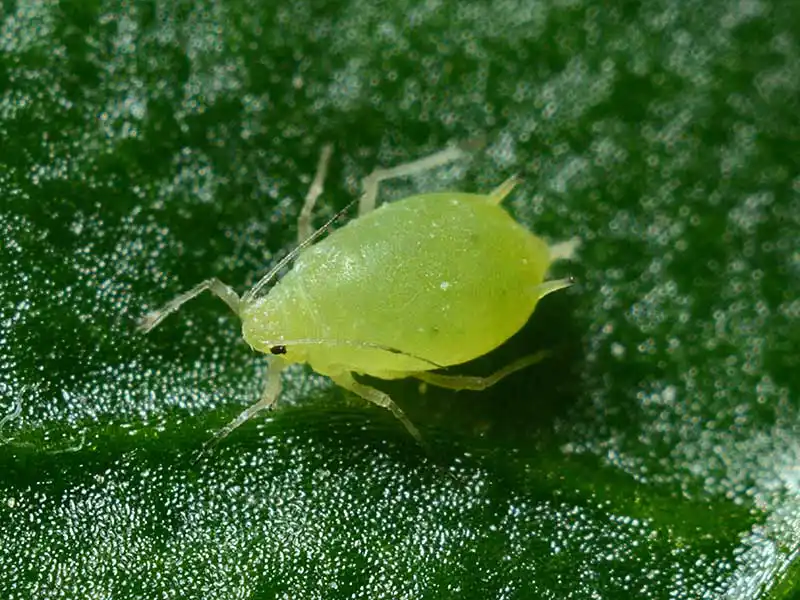

Ghost peppers are susceptible to certain pests and diseases that can affect their growth and yield. Aphids are probably your most likely pest concern when growing ghost peppers, or any other variety of pepper for that matter. Below is a list of common pests and diseases and how to treat them.
| Pest/Disease | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Curling leaves, distorted growth, sticky residue | Spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil, introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings |
| Whiteflies | Yellowing leaves, white powdery spots, flying insects when disturbed | Use yellow sticky traps, spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil, introduce beneficial insects like parasitic wasps |
| Spider Mites | Fine webbing, yellowing leaves, stunted growth | Spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil, increase humidity, isolate affected plants |
| Mealybugs | White cottony masses on stems and leaves, sticky residue | Remove with cotton swabs dipped in alcohol, spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil |
| Fungus Gnats | Tiny flying insects, larvae in soil, yellowing leaves | Allow soil to dry out between watering, use yellow sticky traps, apply beneficial nematodes to soil |
| Powdery Mildew | White powdery spots on leaves, stems, and flowers | Remove infected plant parts, spray with fungicidal soap or neem oil, improve air circulation |
| Leaf Spot | Brown or black spots on leaves, yellowing and wilting | Remove infected plant parts, spray with fungicidal soap or copper-based fungicide |
| Blossom End Rot | Dark, sunken areas on the bottom of fruit | Ensure consistent watering, provide adequate calcium through soil amendments or foliar sprays |
| Root Rot | Yellowing, wilting, and rotting of roots | Improve drainage, avoid overwatering, apply fungicide to soil |
Note: Proper identification of pests and diseases is crucial for effective treatment. Always read and follow the instructions on the label of any pesticide, fungicide, or other treatment used. Prevention and early intervention are key in managing pepper pests and diseases in your garden.
Harvesting Ghost Peppers (Bhut Jolokia)
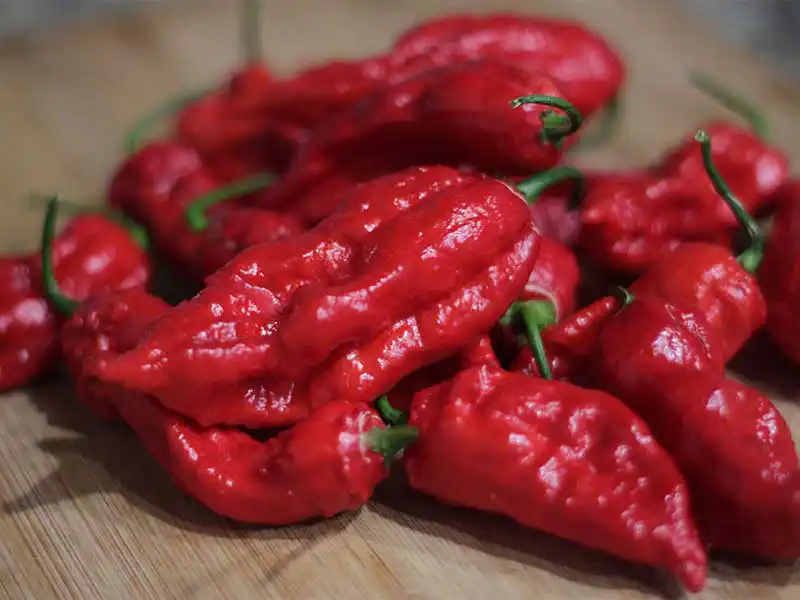

Ghost peppers typically take about 90-120 days to mature from seedling to harvest. The peppers start out green and gradually change color to red as they mature. The peppers can be harvested when they have fully ripened into a deep red color. The stems can be easily snapped or cut from the plant.
The heat of peppers comes from the capsaicin oil inside them. Generally speaking, you can handle peppers without coming in contact with that oil. However, you could potentially break open a pepper while harvesting so don’t touch your eyes and be sure and wash your hands with liquid dish detergent to break down the oils.
Best practice is using gloves and washing your hands thoroughly after handling ghost peppers. Better safe than sorry. Ghost peppers are extremely hot and can cause skin and eye irritation.
Conclusion
Growing ghost peppers from seed can be a challenging but rewarding experience. By providing the right growing conditions, including ample sunlight, warm temperatures, well-drained soil, and proper watering and fertilization, you can successfully grow ghost peppers in your garden. Be mindful of pests and diseases, and practice good sanitation to prevent their occurrence. With patience and care, you can enjoy the fiery flavor of ghost peppers in your home-cooked meals. Happy gardening!
FAQ: Grow Ghost Peppers
How many ghost peppers does one plant produce?
The yield of ghost peppers per plant can vary depending on growing conditions, but on average, a healthy ghost pepper plant can produce several dozens of peppers at one time and about 100 total for the entire season.
Is ghost pepper hotter than habanero?
Yes, ghost pepper (Bhut Jolokia) is considered to be hotter than habanero peppers. Ghost peppers have a Scoville heat rating that ranges from 800,000 to over 1 million, while habanero peppers typically have a heat rating of 100,000 to 350,000 Scoville units.
Can you eat green ghost peppers?
Yes, you can eat green ghost peppers. While they are usually harvested when they turn red, ghost peppers can also be consumed when they are green. However, keep in mind that green ghost peppers are still extremely hot and should be used with caution in cooking or consumed in small amounts.
Can you freeze ghost peppers whole?
Yes, you can freeze ghost peppers whole. To freeze ghost peppers, simply wash and dry them, then place them in a sealed container or freezer bag and store in the freezer for up to 6 months. Freezing can help preserve the heat and flavor of ghost peppers for future use in cooking or seasoning.
How do you winterize a ghost pepper plant?
Trim the plant back to a manageable size leaving only a few main stems and minimum foliage. Cut the branches off just above a node (the attachment point of leaves). Prune the roots back as well to fit into a container. The container size for overwintering a mature ghost pepper plant is about 3 gallon. Place the plant in a dimly lit location such as near a basement window, and water sparingly. Be sure to remove any dead leaves or debris that may attract pests or cause disease during the winter months.