Vegetable Gardening
Pepper Flowers to Peppers: Does Every Bloom Bear Fruit?
Have you ever wondered how peppers actually grow? Do all pepper flowers eventually turn into peppers? In this article, we will explore the fascinating process of pepper growth and answer this common question.
The Life Cycle of a Pepper Plant
Like many other plants, peppers go through a specific life cycle that involves flowering and fruiting. Understanding this cycle can help us better understand why not all pepper flowers turn into peppers.
The life cycle of a pepper plant begins with the germination of seeds. Once the seeds sprout, they develop into seedlings and eventually grow into mature plants. During the growing season, pepper plants produce flowers, which are essential for the production of peppers.
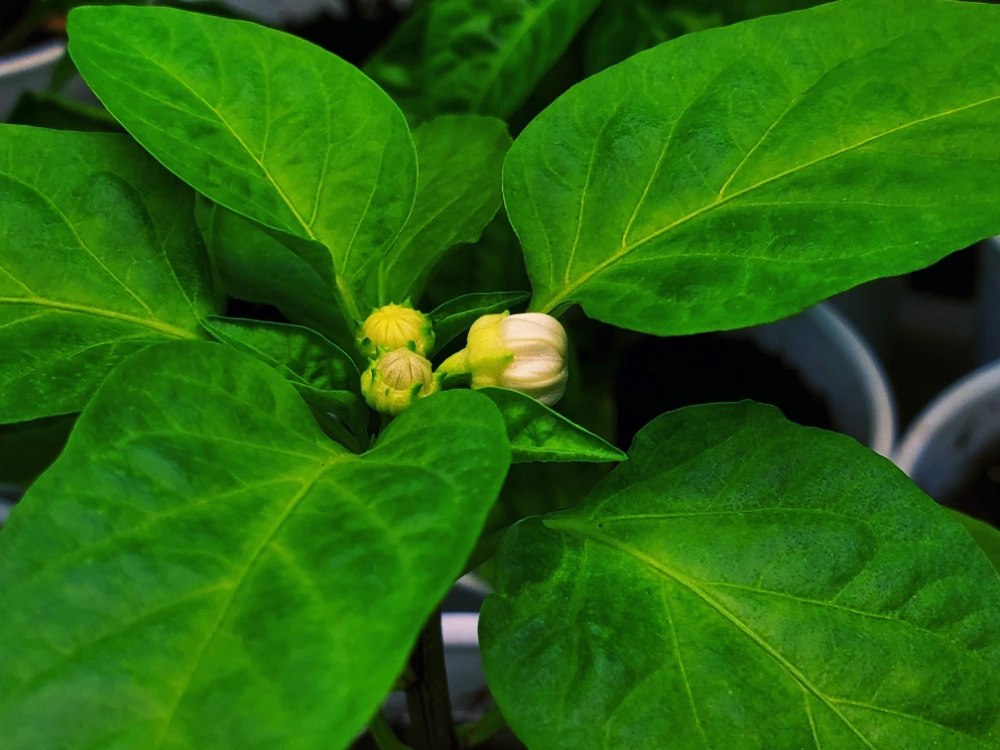
The Role of Pepper Flowers
Pepper flowers play a crucial role in the reproduction of the plant. They contain both male and female reproductive organs, making them self-pollinating. The male part of the flower, called the stamen, produces pollen, while the female part, called the pistil, contains the ovary where the seeds develop.
When a pepper flower is pollinated, either by wind, insects, or even by shaking the plant, the pollen from the stamen fertilizes the ovary in the pistil. This fertilization process is necessary for the development of peppers.
Why Don’t All Pepper Flowers Turn Into Peppers?
While pepper flowers have the potential to turn into peppers, not all flowers successfully develop into fruit. There are several reasons why this may occur:
- Poor pollination: If the flowers are not adequately pollinated, the fertilization process may not occur, resulting in the flower withering and falling off without producing a pepper.
- Environmental factors: Factors such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, or drought can affect the pollination process and hinder the development of peppers.
- Pest damage: Pests, such as aphids or mites, can damage the flowers, preventing them from developing into peppers.
- Disease or nutrient deficiencies: Certain diseases or nutrient deficiencies can impact the overall health of the plant, including its ability to produce fruit.
Maximizing Pepper Production
If you’re growing peppers in your garden and want to maximize your pepper production, there are a few steps you can take:
- Provide proper pollination: Encourage pollinators, such as bees, to visit your garden by planting flowers that attract them. You can also gently shake the pepper plants to aid in pollination.
- Maintain optimal growing conditions: Ensure that your pepper plants receive adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients to promote healthy growth and fruit development.
- Monitor for pests and diseases: Regularly inspect your pepper plants for any signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures to control them.
By following these steps, you can increase the chances of your pepper flowers developing into delicious peppers.
In Conclusion
While not all pepper flowers turn into peppers, they play a vital role in the reproductive cycle of the plant. Factors such as poor pollination, environmental conditions, pests, and diseases can affect the development of peppers. By understanding the life cycle of pepper plants and taking steps to maximize pepper production, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of this flavorful vegetable.